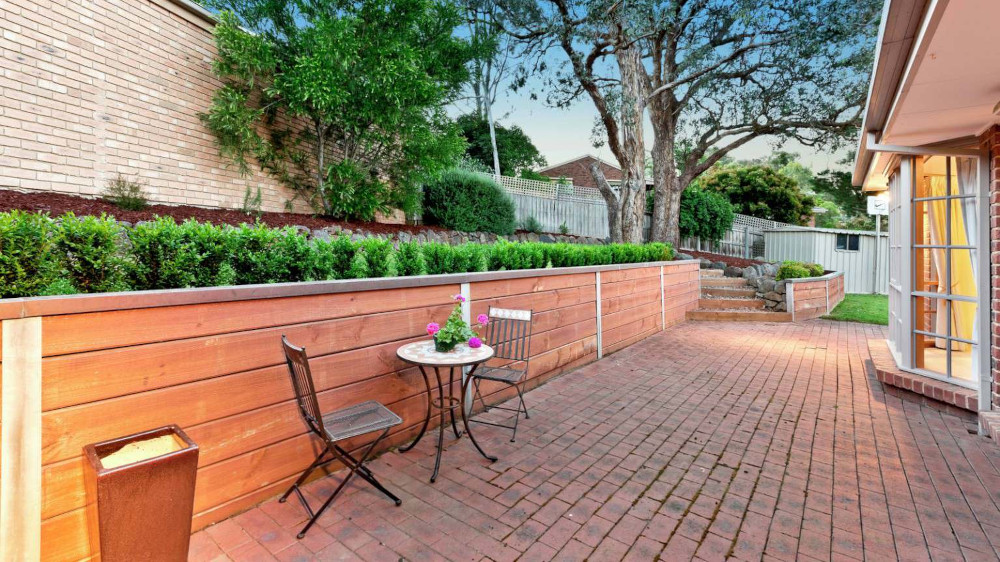
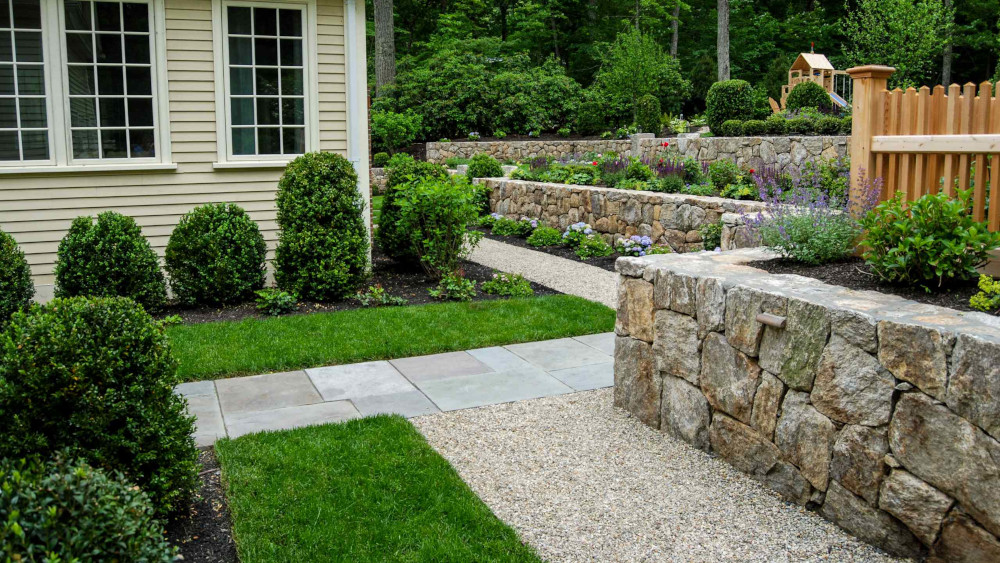
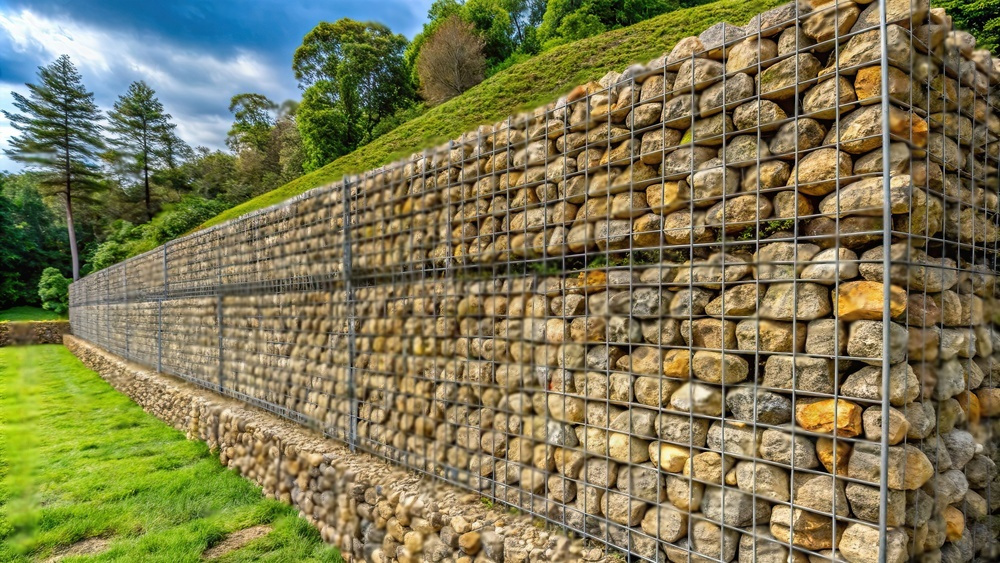
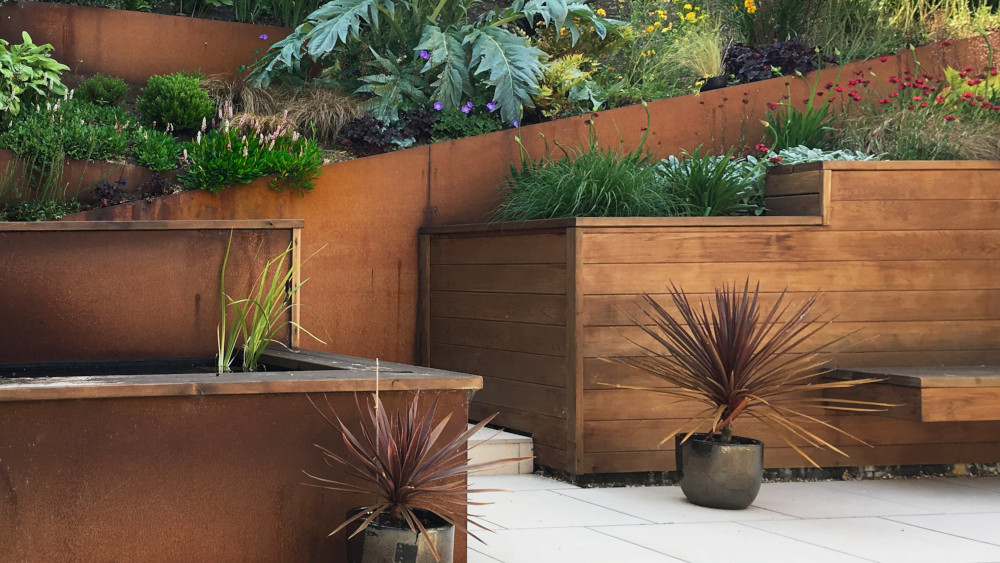
Outdoor living spaces have become essential for New Zealand homeowners seeking to extend their homes into nature, maximize available land, and increase property value. While retaining walls are commonly associated with erosion control and structural support, they also play a significant role in defining, beautifying, and enhancing outdoor areas. From terracing sloped properties to framing patios and gardens, retaining walls can transform a backyard into a versatile and welcoming outdoor living space.
In this blog, we’ll explore the many ways retaining walls can be used to create outdoor living spaces, the materials and designs available, and essential maintenance tips for keeping them looking pristine. Let's delve into how retaining walls can help bring your outdoor vision to life in a sustainable and functional way!
1. The Advantages of Retaining Walls for Outdoor Living Spaces
Retaining walls offer several advantages that go beyond soil stabilization. They can:
- Increase Usable Space: By building terraces or leveling sloped areas, retaining walls create flat spaces ideal for patios, gardens, and seating areas. This is especially valuable for New Zealand homes with uneven or hilly landscapes.
- Add Definition and Structure: Retaining walls define and separate outdoor areas, which can make your garden look more organized and visually appealing.
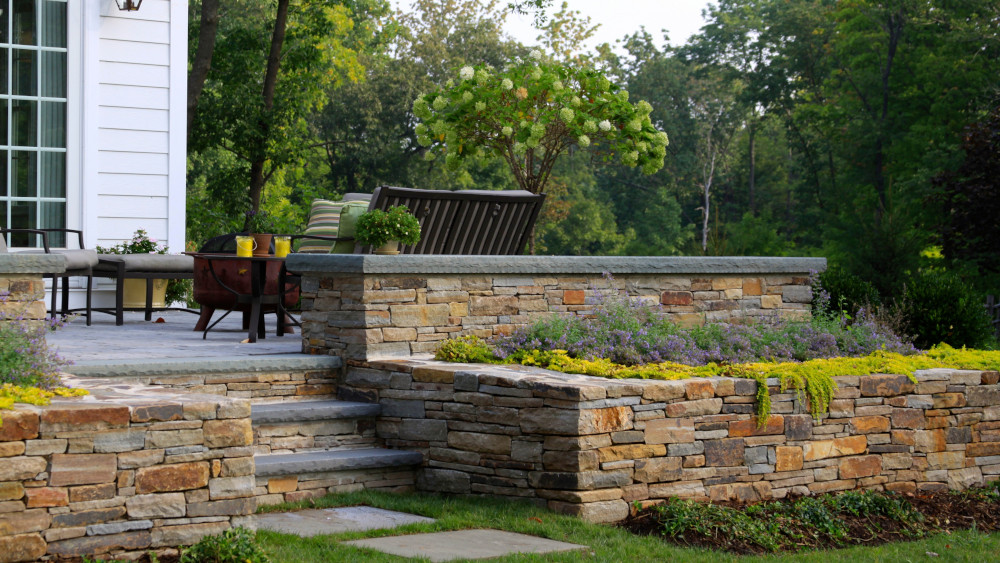
- Enhance Aesthetics: Available in a range of materials like timber, stone, and concrete, retaining walls can match any aesthetic, from rustic to modern.
- Increase Property Value: Well-designed outdoor spaces can significantly boost your property’s value, making it more attractive to potential buyers.
2. Choosing the Right Retaining Wall for Your Outdoor Space
When creating outdoor living spaces with retaining walls, the choice of materials, style, and height is essential. Each factor will affect both the function and aesthetics of your wall.
Popular Retaining Wall Materials in New Zealand
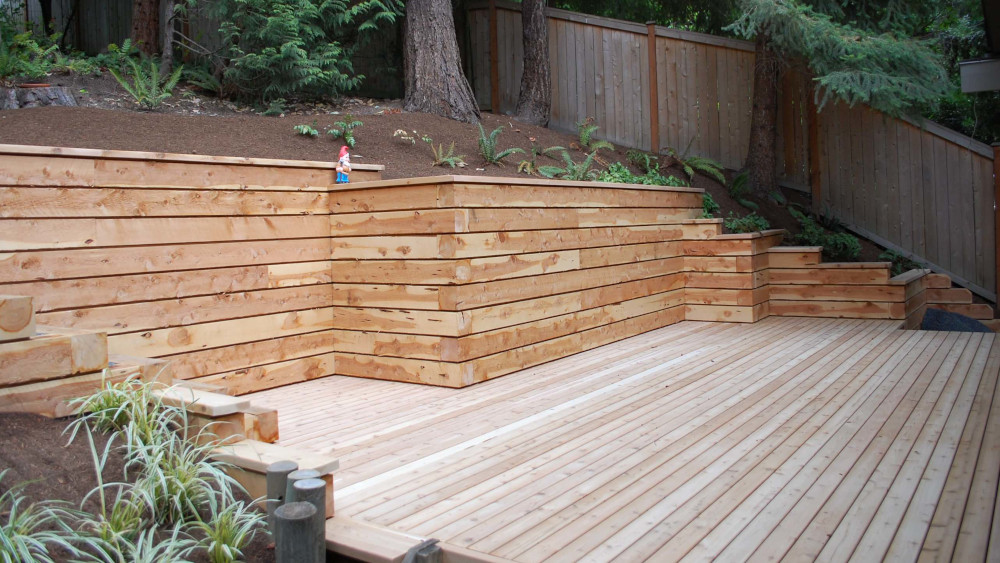
- Timber: Timber walls blend well with natural landscapes, giving a warm and rustic feel. Treated timber is resistant to moisture, but routine maintenance is essential.
- Concrete Blocks: These are versatile and come in various colors and textures. Concrete block walls are durable, low-maintenance, and well-suited for modern designs.
- Stone: Natural stone walls add elegance and charm, ideal for creating focal points in your garden or patio. However, they tend to be more costly and labor-intensive to install.
- Gabion: Gabion walls, made of metal cages filled with rocks, create a rugged, industrial look that suits modern outdoor designs while providing excellent drainage.
Types of Retaining Wall Designs
- Terraced Walls: Ideal for sloped properties, terraced retaining walls create multiple levels, which can be used for planting areas, seating, or pathways.
- Freestanding Walls: Low retaining walls can serve as freestanding barriers that frame patios, dining spaces, or outdoor kitchens.
- Curved Walls: Curved retaining walls add a dynamic, natural feel to your landscape, making pathways or seating areas feel more inviting.
3. Ideas for Creating Functional Outdoor Living Spaces
Outdoor Dining Area
A flat area created with retaining walls is an ideal spot for an outdoor dining area. Install a timber or concrete retaining wall to define the space, then add a sturdy dining table, chairs, and weather-resistant décor. To elevate the space, consider adding lighting or a pergola for shade.
Garden Beds and Green Spaces
Retaining walls can help organize garden beds and create a series of planting areas at different levels. This layered effect is particularly appealing for New Zealand properties with native plants, flowers, or even small fruit trees, making the area feel lush and inviting.
Outdoor Kitchen or BBQ Zone
For those who love outdoor cooking, a retaining wall can separate a BBQ area from the rest of the backyard, creating a defined space for grills, prep tables, and storage. Opt for durable materials like stone or concrete, which are more resistant to heat and weathering.
Seating and Lounge Areas
A low retaining wall can double as seating around a fire pit or outdoor lounge area. This approach saves space and creates a seamless look. Add cushions to make the seating comfortable, and consider using concrete or stone for a modern aesthetic.
Terraced Gardens
On sloped properties, a series of terraced retaining walls can create garden "rooms," each serving a unique function such as a reading nook, a play area, or a small herb garden. Terraced walls not only maximize space but also add depth and visual interest.
Walkways and Steps
Retaining walls can be used to frame walkways and steps, connecting different areas of your outdoor space. This is especially useful on sloped properties, where steps may be necessary for easy access. A combination of materials, like timber for the steps and stone for the walls, can create a visually appealing contrast.
4. Considerations for Building Retaining Walls in New Zealand
Before starting your project, there are several factors specific to New Zealand landscapes and weather conditions to keep in mind.
Drainage
Proper drainage is essential for retaining walls, especially in New Zealand, where heavy rainfall can affect soil stability. Ensure your retaining wall includes a drainage solution, like gravel backfill or weep holes, to prevent water from building up behind the wall.
Compliance and Regulations
Retaining walls over a certain height may require permits, depending on your local council’s regulations. Consulting with a professional landscaper will ensure that your project meets all compliance standards.
Material Selection for Coastal Areas
For properties near the coast, choose materials that are resistant to salt and humidity, like treated timber or marine-grade concrete. This will extend the lifespan of your wall and help it withstand coastal conditions.
5. Maintaining Your Retaining Wall
To keep your retaining wall looking great and functioning well over time, follow these maintenance tips:
- Regular Inspections: Check for signs of erosion, cracks, or bulging. Address these issues early to prevent more significant problems.
- Cleaning: Remove dirt, moss, and debris to keep your wall looking clean and fresh. Pressure washing can help with tougher stains on concrete or stone.
- Vegetation Control: Avoid planting large trees or shrubs too close to your wall, as their roots can cause structural damage. Instead, choose smaller plants or vines that won’t interfere with the wall's stability.
6. Working with a Professional
Designing and constructing retaining walls requires skill and an understanding of the land's unique challenges. Working with a professional landscaper ensures that your wall is built safely, meets all New Zealand regulations, and enhances the visual appeal of your outdoor space. Professionals can also provide guidance on material selection, drainage solutions, and maintenance tips tailored to your property.
Final Thoughts
Retaining walls offer more than just structural support for your property. When thoughtfully designed, they can transform outdoor spaces, create functional zones, and enhance the overall look of your landscape. Whether you’re looking to create a peaceful garden nook, an inviting dining area, or a stylish patio, retaining walls are versatile tools that bring both form and function to your outdoor living spaces.
Ready to Transform Your Space?
At Retaining Walls by LandscapingHQ, we specialize in crafting retaining walls that enhance and protect your outdoor spaces. If you're ready to elevate your landscape with a functional and beautiful retaining wall, get in touch with us today to start your project. Let us help you bring your outdoor vision to life with expert solutions tailored to your needs!
If you own a sloped property in New Zealand, you may already be aware of the challenges that come with maintaining a beautiful and functional landscape on uneven ground. Sloped landscapes are prone to soil erosion, water runoff issues, and limited usable space. Retaining walls offer a practical and visually appealing solution for addressing these issues, transforming your property into a more accessible and stable outdoor area. This comprehensive guide explores how retaining walls can protect your sloped landscape, their benefits, types, and key considerations for installation and maintenance. Whether you’re looking to prevent erosion or enhance the aesthetics of your landscape, retaining walls are a valuable addition to any sloped property.
Why Use Retaining Walls for Sloped Properties?
Retaining walls are designed to hold back soil on uneven terrain, creating level areas and preventing the natural downward movement of soil. On sloped properties, retaining walls provide both structural support and aesthetic appeal, allowing homeowners to create usable outdoor spaces while protecting their land from erosion.
Key reasons to consider retaining walls on a sloped property include:
- Erosion Control: Slopes are vulnerable to soil erosion, especially during heavy rainfall. Retaining walls help stabilize the soil, preventing it from washing away and protecting the foundation of your home and other structures.
- Increased Usable Space: Retaining walls create flat terraces, making it possible to incorporate garden beds, patios, or even play areas on previously unusable terrain.
- Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal: Well-designed retaining walls can add visual interest to your landscape, enhancing curb appeal and property value.
- Improved Drainage: With proper drainage systems, retaining walls help redirect water runoff, preventing puddling and erosion in other areas of your property.
Types of Retaining Walls for Sloped Properties
There are various types of retaining walls, each with unique characteristics and benefits suited to different landscapes and design preferences. Here are some common types used for sloped properties in New Zealand:
- Gravity Retaining Walls
Gravity walls rely on their mass to hold back soil and are typically built using materials like stone, concrete, or large blocks. They are ideal for lower-height walls and are often chosen for their natural look. Gravity walls are a great option for New Zealand landscapes, where blending with natural surroundings is often a priority. - Cantilever Retaining Walls
Cantilever walls are reinforced concrete walls with a unique “L” or “T” shape that extends into the soil for additional support. These walls can withstand higher loads and are ideal for taller structures. They provide excellent stability on steep slopes but require a solid foundation, which may increase installation time and cost. - Segmental Retaining Walls (SRWs)
Segmental retaining walls use interlocking blocks or bricks, providing flexibility in design and excellent drainage. SRWs are easy to install and are especially suitable for small to medium-sized walls. They work well for creating tiered terraces, making them a versatile choice for residential properties. - Timber Retaining Walls
Timber walls are made from treated wood and are a popular choice for shorter walls and garden beds. While timber walls may not last as long as stone or concrete walls, they offer a more rustic look and are an economical option for homeowners. Regular maintenance is essential to prevent wood rot, especially in New Zealand’s wet climate. - Rock or Boulder Retaining Walls
Rock retaining walls provide a natural, rugged look that blends seamlessly with New Zealand’s landscape. These walls are constructed by stacking large rocks or boulders, which can withstand significant pressure and provide good drainage. They are perfect for informal designs and are particularly popular in rural or native-styled gardens. - Gabion Walls
Gabion walls are made by filling wire cages with rocks, stones, or other materials. They’re durable, eco-friendly, and allow water to flow freely through them, which reduces erosion pressure. Gabion walls offer a unique, industrial look that fits well with modern landscapes.
Steps for Building a Retaining Wall on a Sloped Property
Constructing a retaining wall on a slope requires careful planning and proper construction techniques to ensure its effectiveness and longevity. Here’s a step-by-step outline for building a retaining wall on a sloped property:
Step 1: Plan and Design
- Assess the Site: Evaluate the slope, soil type, and any drainage requirements. This assessment will help determine the height and type of wall you need.
- Choose a Design: Decide on the style, materials, and layout of the wall. Consider how the retaining wall will complement the rest of your landscape.
- Consult Local Regulations: Check with local authorities regarding building codes and regulations for retaining walls. Walls over a certain height may require permits or professional engineering.
Step 2: Prepare the Site
- Clear the Area: Remove any vegetation, rocks, or debris from the site. It’s essential to have a clean, stable base to build on.
- Level the Ground: Dig a trench where the wall will sit. This trench should be deep enough to accommodate the base materials, providing stability for the wall.
Step 3: Install a Solid Base
- Add Base Material: Fill the trench with a layer of compacted gravel or crushed stone. This base material will help support the wall and improve drainage.
- Compact the Base: Use a tamper or plate compactor to compact the base material. A solid, well-compacted base is crucial to the stability of the wall.
Step 4: Build the Wall
- Lay the First Course: Start with the bottom layer of blocks or stones, ensuring they are level. This first layer sets the foundation for the rest of the wall, so take your time to get it right.
- Continue Laying Courses: Stack each subsequent layer according to your chosen design. If you’re using interlocking blocks, follow the manufacturer’s instructions for staggered layering.
- Backfill as You Go: As you build, backfill the wall with gravel or soil to provide additional support. Backfilling also helps with drainage, reducing pressure on the wall.
Step 5: Ensure Proper Drainage
- Install Drain Pipes: Place perforated drain pipes behind the wall to direct excess water away from the structure. Proper drainage is essential to prevent water from accumulating behind the wall, which could lead to structural issues.
- Add Weep Holes: For taller walls, include weep holes to allow water to escape from behind the wall. This reduces hydrostatic pressure on the wall, increasing its lifespan.
Maintaining Your Retaining Wall
Once your retaining wall is in place, routine maintenance will keep it looking and functioning at its best. Here are some essential maintenance tips:
- Inspect Regularly: Check for signs of movement, cracks, or bulging, especially after heavy rains. Addressing these issues early can prevent larger structural problems.
- Clear Debris and Vegetation: Remove leaves, dirt, and plants that may grow on or near the wall. Vegetation can compromise the stability of the wall by trapping moisture.
- Check Drainage Systems: Ensure that drain pipes and weep holes are clear and functioning. Blocked drainage can lead to water buildup, weakening the wall over time.
- Repair Any Damage: If you notice any cracks or loose stones, repair them promptly. Small repairs can prevent more extensive and costly damage down the road.
Benefits of Retaining Walls on Sloped Properties
Installing a retaining wall on a sloped property provides numerous benefits that go beyond soil retention:
- Enhanced Curb Appeal: A well-constructed retaining wall adds structure and visual interest to your landscape, increasing your property’s appeal and value.
- Increased Functional Space: Terracing with retaining walls creates usable, flat areas that can be utilized for gardening, seating, or outdoor entertaining.
- Improved Water Management: Retaining walls with proper drainage help manage water runoff, reducing the risk of erosion and flooding in other areas of your property.
- Environmentally Friendly: By reducing erosion, retaining walls help protect the environment by maintaining soil stability and preventing sediment from entering waterways.
Choosing a Retaining Wall Builder in New Zealand
For larger retaining walls or complex projects, it’s often best to work with an experienced retaining wall specialist. Retaining walls require precise engineering and expertise, particularly on sloped properties where soil stability is a concern. When selecting a builder, consider their experience, past projects, and understanding of New Zealand’s specific landscape and environmental requirements.
Conclusion
Retaining walls are a valuable investment for sloped properties, providing both practical and aesthetic benefits. From preventing erosion to creating beautiful terraces, retaining walls transform challenging landscapes into functional and attractive outdoor spaces. Whether you’re looking to protect your property from soil erosion or add more usable space for gardens and entertaining areas, retaining walls offer a versatile solution.
Ready to Protect Your Sloped Property? Contact Retaining Walls by LandscapingHQ!
If you’re considering adding retaining walls to your landscape, Retaining Walls by LandscapingHQ is here to help. Our expert team specializes in designing and constructing durable, visually appealing retaining walls tailored to New Zealand’s unique terrain. Get in touch today to discuss your project and transform your sloped property into a stunning and functional outdoor space.
Retaining walls are a versatile landscaping solution that can serve both practical and aesthetic purposes. In New Zealand, where gardens are a celebrated part of residential landscapes, using retaining walls to create garden beds can elevate the look of your outdoor space while helping to manage challenging terrain. Whether you're looking to make the most of a sloped yard or add layers of interest to a flat area, retaining walls offer a flexible way to enhance your garden's beauty and functionality. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to use retaining walls for garden beds, covering design tips, practical benefits, and how to care for these beautiful additions to your garden.
Why Use Retaining Walls for Garden Beds?
Retaining walls are often seen as purely functional structures, but they’re also perfect for creative landscaping projects, especially for garden beds. Here are some key reasons why they’re an excellent choice for New Zealand gardens:
- Maximizing Space on Sloped Land
New Zealand’s diverse landscape often includes hilly or sloped areas, making traditional gardening difficult. Retaining walls can transform sloped land into tiered garden beds, creating flat, usable spaces that support healthy plant growth. - Enhancing Garden Aesthetics
Retaining walls add a level of sophistication to your garden, creating defined, elevated spaces that showcase your plants. With various materials to choose from—like timber, concrete, or stone—retaining walls can complement any garden style. - Improving Soil Retention and Drainage
Retaining walls help control soil erosion and improve drainage, both essential factors for a healthy garden. With proper construction and drainage, retaining walls prevent soil from washing away and help manage water runoff. - Creating Microclimates
The sheltered and elevated garden beds formed by retaining walls can provide ideal microclimates for specific plants. The walls retain warmth from the sun, creating a favorable environment for plants that need extra warmth.

Types of Retaining Walls for Garden Beds
There are various retaining wall materials, each offering unique benefits for garden beds. Here’s an overview of popular retaining wall options for New Zealand gardens:
- Timber Retaining Walls
Timber retaining walls are popular for their natural look and affordability. They blend well into garden landscapes and work perfectly for lower garden beds. However, they require regular maintenance to prevent rotting and damage from pests. - Concrete Block Walls
Concrete blocks are incredibly durable and offer a modern aesthetic. They can be arranged in various shapes and heights, making them a flexible choice for multi-level garden beds. Concrete walls require less maintenance than timber and can withstand harsh weather conditions. - Stone or Rock Walls
Natural stone walls create a rustic, timeless look that blends beautifully into New Zealand’s natural landscapes. Stone retaining walls are highly durable and provide excellent drainage, making them ideal for large or high garden beds. - Gabion Walls
Gabion walls are created by filling wire cages with rocks or other materials. They provide a unique, industrial look and are incredibly sturdy. Gabions are also environmentally friendly, allowing water to flow through them naturally, reducing erosion.
Designing Garden Beds with Retaining Walls
Designing garden beds with retaining walls requires a balance of form and function. Here are some tips to guide your design process:
1. Choose the Right Height and Width
- The height of your retaining walls will depend on your garden’s layout and the type of plants you wish to grow. Low walls (under 1 meter) are ideal for flowers and herbs, while higher walls work well for shrubs or trees.
- Ensure that the width of the garden bed is sufficient to allow plants enough space for root growth.
2. Use Multi-Tiered Walls for Added Interest
- Creating multiple tiers with retaining walls adds depth to your garden and increases planting space. Each level can be used for different plant types, allowing for a variety of colors and textures.
- For example, the top tier could be for flowering plants, the middle for shrubs, and the bottom for ground cover or herbs.
3. Plan for Drainage
- Proper drainage is crucial to prevent water buildup behind the wall, which could weaken its structure. Incorporate gravel and drainage pipes behind each wall to ensure that excess water flows away from the garden bed.
4. Select a Cohesive Material and Style
- Choose a material that complements the overall style of your home and garden. For a rustic look, stone or timber works best. For a modern garden, concrete or smooth stone provides a sleek appearance.
5. Incorporate Seating or Pathways
- Retaining walls can also double as seating areas, especially if you’re building lower walls. Adding seating or integrating pathways alongside your garden beds can enhance the usability of the space.
Choosing Plants for Retaining Wall Garden Beds
The elevated and well-drained nature of retaining wall garden beds makes them suitable for a wide range of plants. However, certain plants are better suited to these environments:
- Native New Zealand Plants
Native plants such as Hebe, Pseudopanax, and Carex are low-maintenance and thrive in New Zealand’s climate. They’re also beneficial for supporting local biodiversity. - Flowering Perennials
Plants like lavender, geraniums, and daisies add color and attract pollinators to your garden. They are hardy and can thrive in the well-drained soil of raised beds. - Herbs and Edible Plants
Herbs such as rosemary, thyme, and sage are perfect for retaining wall beds. The elevated position provides good drainage, and they’re easy to access when cooking. - Succulents and Drought-Tolerant Plants
For areas that receive full sun, consider drought-tolerant plants like succulents, yucca, and sedums. They’re low-maintenance and add texture to the garden.
How to Build and Maintain Garden Beds with Retaining Walls
Building Retaining Wall Garden Beds
If you’re considering building a retaining wall garden bed yourself, keep in mind these important steps:
- Excavation and Foundation
Start by excavating the area and creating a stable foundation. A compacted gravel base is essential for wall stability. - Layering and Backfilling
Once the wall is in place, layer soil with compost or organic matter to create a nutrient-rich environment for plants. Add a layer of gravel at the base for extra drainage. - Install Drainage Pipes
Drainage pipes or weep holes are necessary to prevent water buildup, which can weaken the wall structure.
Maintaining Your Retaining Wall Garden Beds
Regular maintenance will help your garden beds thrive and your retaining walls stay sturdy:
- Inspect the Wall
Check for signs of wear, cracks, or leaning. Catching these issues early can prevent costly repairs. - Clean and Weeds Control
Remove any weeds that may grow between stones or blocks and clear debris from the wall surface to prevent plant damage. - Adjust Soil Levels
Over time, soil may settle. Periodically add new soil and compost to keep the bed level and nutrient-rich.
Benefits of Retaining Wall Garden Beds
Garden beds with retaining walls offer a range of benefits beyond aesthetic appeal. These functional advantages make them a wise choice for New Zealand homeowners:
- Increased Planting Space: They enable gardening in areas that would otherwise be too steep or uneven.
- Improved Soil Health: The addition of retaining walls creates deep beds that encourage root growth, and they prevent soil erosion.
- Enhanced Property Value: Well-designed retaining walls and garden beds can significantly boost your property’s curb appeal and market value.
- Reduced Soil Erosion: Retaining walls stabilize soil on slopes, preventing the runoff that leads to soil loss.
Conclusion
Creating garden beds with retaining walls is an excellent way to enhance both the beauty and functionality of your outdoor space. By choosing the right materials, designing with purpose, and maintaining your walls, you can build a garden that not only looks stunning but also thrives in New Zealand’s varied climate. From defining your garden’s aesthetic to maximizing space and improving soil quality, retaining wall garden beds are a worthwhile addition for any homeowner.
Ready to Transform Your Garden? Contact Retaining Walls by LandscapingHQ!
If you’re inspired to add garden beds with retaining walls to your property, Retaining Walls by LandscapingHQ is here to help. Our team specializes in designing and building beautiful, durable retaining walls tailored to New Zealand landscapes. Contact us today to discuss your project and get started on creating the garden of your dreams!
Soil erosion is a common concern for property owners, particularly in New Zealand’s varied landscape, which ranges from mountainous regions to coastal plains. This natural process, accelerated by heavy rains and shifting soils, can have serious consequences, including property damage, reduced land usability, and loss of vegetation. One effective way to combat soil erosion is by building retaining walls. These structures not only prevent soil from washing away but also add aesthetic appeal and functional space to your property. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the benefits, types, and construction considerations of retaining walls for erosion control, specifically tailored to the unique needs and environment in New Zealand.
Why Soil Erosion Control is Essential in New Zealand
New Zealand’s diverse geography and climate conditions contribute to a high risk of soil erosion. With frequent rain, especially in the winter months, and areas with steep topography, the risk of erosion is significant, particularly in regions such as the Bay of Plenty, the North Island’s east coast, and certain hilly inland areas. Soil erosion can lead to:
- Property Damage: Uncontrolled erosion can destabilize foundations, causing landslides that threaten structures and safety.
- Reduced Land Usability: Slopes affected by erosion become less stable, reducing the usable area of your property and impacting gardens, pathways, and other outdoor features.
- Environmental Impact: Soil erosion can lead to sedimentation in rivers and streams, impacting water quality, aquatic life, and vegetation.
To address these issues, property owners in New Zealand are increasingly turning to retaining walls, which serve as effective tools in stabilizing soil, controlling erosion, and preserving the natural beauty of the landscape.
The Role of Retaining Walls in Erosion Control
Retaining walls are specially designed to support soil and prevent it from shifting. By creating a barrier, these walls reduce the risk of erosion, protect property structures, and enhance landscaping features. In addition to protecting against erosion, retaining walls help in:
- Managing Water Flow: Proper drainage integrated within retaining walls can redirect water flow, preventing it from destabilizing soil.
- Creating Usable Space: Steeper landscapes become usable with tiered retaining walls, allowing for the development of gardens, pathways, or recreational areas.
- Improving Aesthetics: Retaining walls add visual appeal, creating a more polished look in sloped or uneven areas.
Types of Retaining Walls for Erosion Control in New Zealand
Different types of retaining walls are suited to specific conditions, such as soil type, slope gradient, and water exposure. Here are some common options:
- Gravity Retaining Walls
- These walls rely on their weight and mass to hold soil in place. Built from heavy materials like concrete, stone, or bricks, gravity walls are ideal for smaller projects and areas with mild slopes. For taller walls, additional reinforcement may be required.
- Cantilever Retaining Walls
- Supported by a concrete base that extends under the soil, cantilever walls are well-suited to handle heavier loads and higher slopes. These walls distribute weight efficiently, making them a popular choice for properties with more severe erosion risks.
- Segmental Retaining Walls
- Built from interlocking concrete blocks, segmental walls are versatile and allow for quick, easy installation. This type is especially useful for property owners looking for DIY options that can still manage moderate erosion issues.
- Gabion Retaining Walls
- Gabion walls consist of wire baskets filled with rocks or stones. They are highly effective at erosion control as they allow water to pass through, reducing hydrostatic pressure. Gabions are ideal for coastal properties and areas prone to water accumulation.
- Timber Retaining Walls
- Timber walls, often made from treated pine or hardwood, are a cost-effective solution suitable for moderate slopes. Although they may not last as long as other materials, timber retaining walls blend well with natural surroundings and are popular for residential landscaping projects.
- Sheet Pile Retaining Walls
- Commonly used in commercial and waterfront areas, sheet pile walls consist of long, interlocking panels driven deep into the ground. These walls are best for properties with limited space or where erosion due to water flow is a primary concern.
Key Factors to Consider Before Building a Retaining Wall for Erosion Control
Constructing a retaining wall in New Zealand requires careful planning and knowledge of local soil and weather conditions. Here are some essential considerations:
- Soil Type and Composition
- Different soil types respond to erosion differently. For instance, clay soils retain water, making them susceptible to pressure build-up, while sandy soils drain easily but can shift quickly. Understanding your soil type will help you choose the best retaining wall type and design.
- Slope Gradient and Wall Height
- Steeper slopes typically require taller and more reinforced retaining walls. However, New Zealand regulations may restrict wall heights without proper council consent, so it's important to check local codes before starting your project.
- Drainage Systems
- Poor drainage can lead to water pressure build-up behind the wall, causing it to fail. Incorporate drainage solutions like weep holes, gravel backfills, or French drains to ensure water flows away from the wall.
- Weather Patterns
- Given New Zealand’s variable weather, it’s essential to plan for both heavy rainfall and dry spells. Ensure that your wall can handle seasonal changes without weakening or collapsing.
- Council Regulations and Permits
- New Zealand councils often have specific regulations regarding retaining walls, particularly for taller structures. Depending on the location and height of your wall, you may need a permit and engineering certification. Always consult your local council for guidelines before starting.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Retaining Wall for Erosion Control
- Assess Your Site
- Survey the area, noting soil type, slope, drainage, and the position of any existing structures. Consult with a landscaping or engineering professional if needed.
- Choose the Right Materials
- Select materials that complement your property, fit your budget, and provide the necessary strength and durability for erosion control. Concrete blocks, stone, and timber are all popular choices in New Zealand.
- Prepare the Foundation
- A solid foundation is crucial for stability. Excavate the area to create a level base, and lay a compacted gravel foundation to prevent settling.
- Install Drainage Solutions
- Set up drainage pipes or add gravel behind the wall to direct water away. This step is essential to prevent hydrostatic pressure from weakening the structure.
- Build the Wall
- Follow proper construction techniques for the chosen material. For interlocking blocks, ensure each row is staggered. For timber, ensure proper anchoring with steel rods or rebar.
- Backfill the Wall
- As you build, backfill with gravel or soil to provide additional stability. Be careful to avoid compacting soil too tightly, as this can affect drainage.
- Finishing Touches
- Add landscaping features like plants or ground cover to help absorb water and reduce erosion. This also adds a natural aesthetic to your retaining wall.
Maintenance Tips for Long-Lasting Erosion Control
Retaining walls require regular upkeep to ensure they continue to protect against erosion effectively:
- Inspect for Cracks or Leaning: Check periodically for signs of movement, cracks, or bulging, and address these issues promptly.
- Clear Drainage: Ensure that drainage channels are free from debris, which could obstruct water flow and lead to pressure build-up.
- Control Vegetation: While plants help with erosion control, avoid large shrubs or trees with roots that may compromise wall stability.
Sustainable Erosion Control: Native Plants and Ground Cover
In addition to retaining walls, incorporating native plants and ground cover can further stabilize soil. Native New Zealand species like Muehlenbeckia axillaris (Creeping Pohuehue) or Coprosma acerosa thrive in local climates and naturally resist erosion. These plants can be planted near retaining walls or on slopes to create a sustainable, multi-layered approach to erosion control.
Cost of Building Retaining Walls in New Zealand
The cost of building a retaining wall in New Zealand varies based on materials, wall height, and labor. Timber retaining walls might start around NZD 150 per square meter, while more durable options like concrete or stone can range from NZD 300 to 600 per square meter. Additional expenses may include drainage systems, permits, and professional consultations.
Conclusion: Investing in Erosion Control for Your Property
Erosion is a natural process, but with careful planning and the right solutions, you can protect your property from its effects. Retaining walls offer a durable, effective, and often visually appealing way to prevent soil erosion, providing peace of mind and enhancing property value. By choosing a retaining wall suited to your landscape, integrating proper drainage, and following regular maintenance, you’ll enjoy a secure and beautiful outdoor space, even in the face of New Zealand’s unpredictable weather.
Whether you’re looking to stabilize a steep slope or create usable space on your property, retaining walls for erosion control are an investment in the longevity and functionality of your landscape. Contact LandscapingHQ today to explore our expert solutions for retaining walls that protect your property and enhance its beauty, built to withstand New Zealand’s unique environment. Safeguard your landscape for years to come with Retaining Walls by LandscapingHQ!
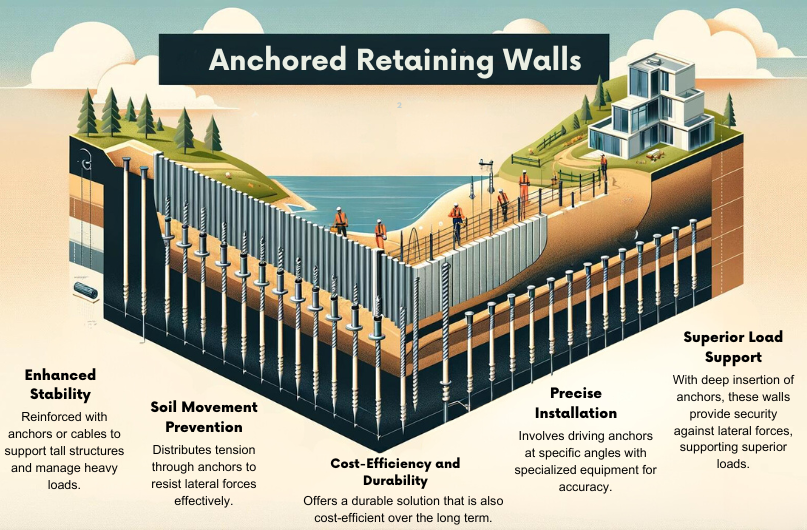
Anchor retaining walls, essential for stabilizing terrain, rely on anchoring cables or rods for stability and support. These walls prevent downhill soil movement by distributing tension through anchors, resisting lateral forces with deep insertion, and transferring loads securely. The installation process involves driving anchors at specific angles, ensuring stability with precise alignment, and using specialized equipment for accuracy. If you seek to understand more about the components, design elements, advantages, and applications of anchored retaining walls, there is a wealth of information available on these topics.
Main Points
- Anchored retaining walls are reinforced with anchors or cables for stability.
- They prevent downhill soil movement and support tall structures effectively.
- Installation involves driving anchors at specific angles and ensuring deep insertion.
- Load distribution through anchors provides security against lateral forces.
- Advantages include cost-efficiency, durability, and superior load support.
Anchored Retaining Walls
Anchored retaining walls, reinforced by anchors or cables, are essential structures designed to provide added stability and support, especially for tall walls or those supporting heavy loads. The benefits of anchored walls lie in their ability to prevent soil or materials from moving downhill, thereby ensuring the wall's structural integrity. When considering the design of anchored retaining walls, several key factors need to be considered. The type and spacing of anchors or cables, the depth and inclination of the wall, and the soil conditions all play an important role in determining the effectiveness of the structure.
Design considerations for anchored retaining walls include selecting appropriate anchor materials, such as steel or grouted rods, based on the project's specific requirements. Additionally, the load-bearing capacity of the anchors must be carefully calculated to withstand the forces exerted on the wall. Proper drainage behind the wall is also essential to prevent water buildup, which can compromise the stability of the structure. By carefully addressing these design considerations, anchored retaining walls can effectively support tall structures and heavy loads while ensuring long-term stability.
Components of Anchored Retaining Walls
When considering the components of anchored retaining walls, you must focus on essential elements like:
- Wall design, which determines the overall stability and load-bearing capacity of the structure.
- The anchor system functions to provide the necessary lateral support.
- Structural integrity is pivotal in ensuring the wall's effectiveness in retaining soil or other materials.
Wall Design Elements
One pivotal component of anchored retaining walls is the inclusion of anchoring cables or rods for improved stability. These elements play a vital role in maintaining the structural integrity of the wall by providing lateral support and preventing potential soil movement.
When considering the design of anchored retaining walls, engineers carefully select materials that offer durability and strength, such as reinforced concrete or steel. Design considerations also include the wall's height and depth, typically ranging from 6-18 meters in height and 8-24 centimeters in depth.

Anchor System Function
The anchor system in retaining walls comprises horizontal steel tie rods or steeply raking tie rods, providing essential stability to the structure. These components play a vital role in ensuring the integrity and longevity of the wall. Here are some key functions of the anchor system:
- Anchor tension: The tie rods help to distribute the load evenly along the wall, reducing the risk of failure due to excessive pressure.
- Soil reinforcement: By anchoring the wall into the soil, these systems prevent soil movement and potential collapse.
- Connection to A-frame anchorages: Horizontal tie rods are connected to A-frame anchorages, adding extra support and reinforcement.
- Cable attachment: Cables attached to the wall and anchored in stable structures improve the wall's ability to resist bearing capacity failure.
Structural Integrity Importance
To guarantee the structural integrity of anchored retaining walls, the components play a crucial role in maintaining stability and preventing potential failures. Proper anchoring is of utmost importance for the overall stability of these structures.
Anchored retaining walls benefit greatly from components such as deadman anchors and bearing piles, which are essential for ensuring the stability of thin walls in challenging conditions. Engineers who specialize in geotechnical aspects meticulously design these components to withstand high loads and limited spaces effectively.
The benefits of these components extend to the overall performance and longevity of anchored retaining walls, making them indispensable for the successful construction and functionality of these structures in various geotechnical settings.
Working Principle of Anchored Walls
When installing anchors in an anchored retaining wall, you drive them deep into the soil or rock at an angle to bolster lateral pressure.
This installation method fortifies the wall's stability and structural integrity.
The anchoring system works in conjunction with the wall design to create a durable and effective retaining structure.
Anchor Installation Process
By driving anchors deep into the soil or rock at a specific angle, anchored retaining walls gain lateral support essential for their stability and load distribution.
- Anchors are typically driven at a 15-45 degree angle into the soil or rock.
- The depth of the anchors is vital to provide adequate lateral support.
- Proper alignment of the anchors guarantees ideal load distribution.
- Installation of anchors may involve specialized equipment for precision and efficiency.
Wall Stability Mechanism
The stability mechanism of anchored retaining walls relies on the strategic placement and utilization of anchors or cables for improved structural support and load distribution. Soil stability is achieved by deep insertion of anchors into the soil or rock, effectively resisting lateral forces that could compromise the wall's integrity.
Anchor technology plays a vital role in the overall stability of these walls, allowing them to handle heavier loads and prevent soil movement downhill. By transferring the load from the wall to the anchors, the system guarantees that the structure remains secure and reliable.
This working principle is fundamental in enhancing the wall's capacity to withstand external pressures and maintain its structural integrity over time.
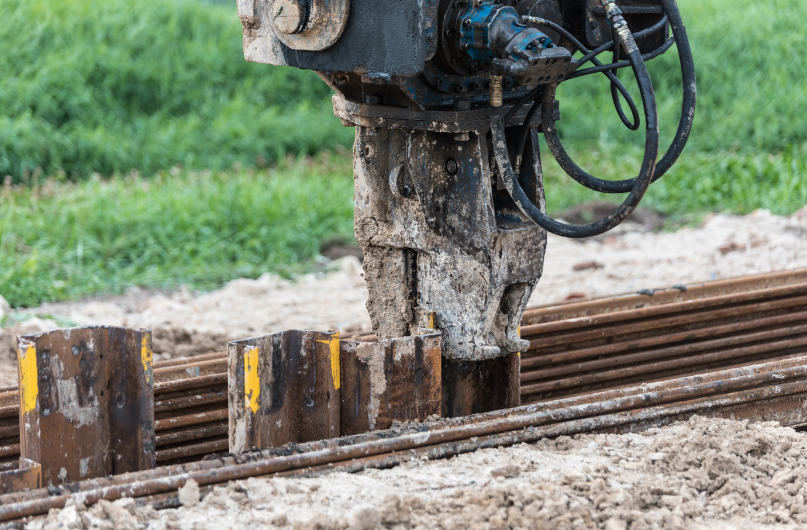
Installation Process of Anchored Walls
To initiate the installation process of anchored walls, begin by preparing the site through soil movement and hole excavation. This important step sets the foundation for the stability of the structure. Once the site is ready, follow these steps:
- Excavation Process: Dig the holes to the required depth and diameter based on the design specifications.
- Soil Compaction: Compact the soil at the bottom of the holes to guarantee a stable base for the anchor blocks.
- Base Material Placement: Lay the necessary base material at the bottom of the holes before installing the anchor blocks.
- Anchor Block Installation: Securely place the anchor blocks in the holes to provide the necessary lateral support for the wall.
Following these steps meticulously is essential to guarantee the strength and stability of the anchored retaining wall. Each step contributes to the overall effectiveness of the anchoring system, providing the necessary support for the wall structure.
Advantages of Anchored Retaining Walls
Maximizing stability and load-bearing capacity, anchored retaining walls offer numerous advantages in construction projects. These walls are cost-efficient due to their durable design, requiring lower maintenance over time. The deeply inserted anchors provide superior load support, enabling them to withstand heavier loads with ease. Their slim profile makes transportation and installation more straightforward compared to bulkier alternatives, improving construction ease.
Additionally, anchored retaining walls are highly durable, ensuring long-term reliability in slope protection and excavation support on construction sites. By combining cost efficiency, durability, enhanced load support, and construction ease, these walls present a versatile solution for various construction challenges.
Whether you need to secure steep slopes or reinforce excavation sites, anchored retaining walls stand out as a practical and reliable choice for maximizing stability and structural integrity in construction projects.
Case Studies of Anchored Retaining Walls
When examining case studies of anchored retaining walls, engineers frequently observe their effectiveness in supporting tall or heavily loaded structures through the integration of anchors or cables for improved stability and load-bearing capacity.
- Case Study Analysis: Engineers conduct in-depth case study analysis to understand the performance of anchored retaining walls in various real-world scenarios.
- Construction Challenges: Identifying and overcoming construction challenges such as limited access, soil conditions, and environmental impacts play a vital role in the successful implementation of anchored retaining walls.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Regular monitoring and maintenance are essential for ensuring the long-term stability and performance of anchored retaining walls.
- Innovation and Advancements: Continuous research and development efforts lead to innovative techniques and advancements in the design and construction of anchored retaining walls.
Why Hire Us for Anchored Retaining Wall Services
When it comes to building a retaining wall, materials and techniques matter. Our team specializes in anchored retaining wall solutions, providing unparalleled expertise and quality construction.
Anchored retaining walls utilize cables or rods anchored deep into the soil to provide exceptional stability, even on steep slopes or in areas with poor soil conditions. The anchors evenly distribute lateral forces and prevent the wall from tipping or sliding. This makes anchored walls an ideal choice for sites where gravity walls would likely fail.
With years of experience, our crew handles every phase of the retaining wall-building process. We evaluate your terrain’s unique challenges, recommend the optimal wall design, procure quality building materials, and leverage specialized equipment for safe installation. Throughout, we remain focused on building attractive, enduring walls tailored to your property’s needs.
Whether you need a small residential wall or a large commercial project, our versatility and technical know-how set us apart. We construct durable anchored retaining walls using various building materials - including concrete, blocks, stone and timber - customized to suit the aesthetics and functionality you desire.
Don’t leave your landscape’s steep terrain or erosion problems unchecked. Our expertise in anchored retaining wall solutions offers reliable stabilization and protection. Contact us today to discuss your site’s needs!
FAQ's
How Do Anchored Retaining Walls Compare to Other Types of Retaining Walls in Terms of Cost and Durability?
When comparing anchored retaining walls to other types, you'll find they offer a cost-efficient solution with improved durability. The deep anchors provide stability and load-bearing capacity, making them a reliable choice for longevity analysis.
Are There Any Limitations or Specific Conditions Where Anchored Retaining Walls May Not Be Suitable for Use?
In certain scenarios, limitations exist for anchored retaining walls due to high groundwater, seismic activity, or corrosive soils. Alternative solutions might be necessary in sites with access issues or unsuitable cohesive soils.
Can Anchored Retaining Walls Be Used in Combination With Other Types of Retaining Wall Systems for Enhanced Stability?
When considering stability in combined systems, anchored retaining walls can be effectively used with various wall types. Construction techniques guarantee compatibility, enhancing overall wall performance. The tie-back system provides added stability in high-load situations.
What Maintenance Is Required for Anchored Retaining Walls to Ensure Long-Term Effectiveness?
To guarantee long-term effectiveness, you should conduct regular inspections for signs of corrosion, monitor soil movement, maintain proper drainage, periodically re-tension anchor rods, and address vegetation growth. If issues arise, seek professional repair promptly.
How Do Environmental Factors Such as Soil Type and Water Drainage Impact the Design and Performance of Anchored Retaining Walls?
Incorporating soil composition and drainage impact is essential for anchored walls. Stability analysis, design considerations, and construction techniques hinge on environmental factors. Performance evaluation guarantees structural integrity. Cost comparison and durability assessment are key for long-term effectiveness.
Conclusion
To sum up, anchored retaining walls are designed to provide stability and support to prevent soil erosion and slope failures. By utilizing anchors to secure the wall to the ground behind it, these structures can withstand significant lateral forces.
The components, working principle, and installation process all contribute to the effectiveness of anchored retaining walls. Their advantages include cost-effectiveness, versatility, and durability. Case studies demonstrate the successful implementation of anchored retaining walls in various projects.
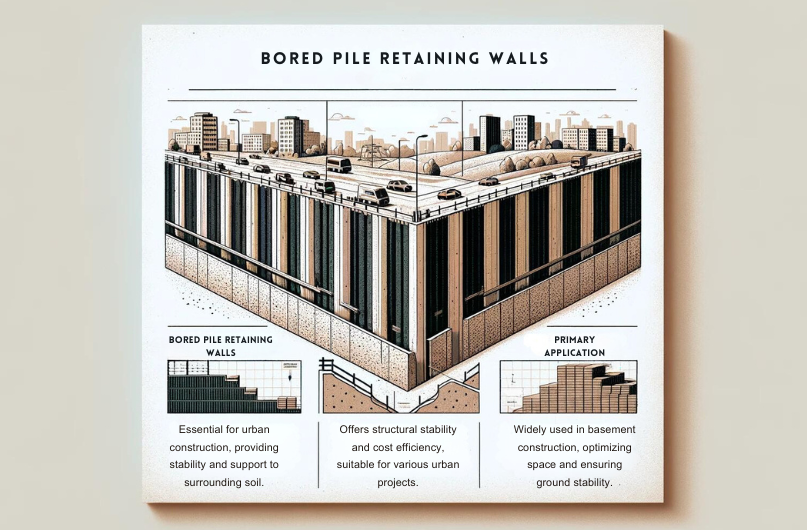
If you've ever wondered how bored pile retaining walls function, imagine a system that not only supports but also stabilizes the earth around it.
These walls, created through a methodical process involving drilling and filling with concrete, play a crucial role in urban environments.
But how exactly do they manage to keep everything in place? Let's unravel the mystery behind these structures that silently safeguard their surroundings, offering a unique perspective on modern engineering solutions.
Key Takeaways
- Bored pile retaining walls use deep foundation elements filled with concrete for structural stability.
- They rely on frictional resistance and reinforcement for load-bearing capacity.
- Advantages include adaptability, cost efficiency, and sustainability in various applications.
- Factors influencing design include soil conditions, reinforcement details, and construction methods.
Advantages of Bored Pile Retaining Walls
When considering bored pile retaining walls, one can't overlook their unparalleled adaptability to diverse design layouts, making them a prime choice for a range of construction needs. Cost efficiency is a significant advantage of bored pile retaining walls. These walls typically require minimal bulk excavation compared to other deep foundation systems, which helps reduce overall construction costs. Additionally, the installation of bored pile retaining walls in restricted spaces minimizes the need for extensive site preparation, further contributing to cost savings.
Moreover, bored pile retaining walls offer environmental benefits. Their ability to be constructed with different thicknesses based on specific site needs ensures that only the necessary materials are used, reducing waste. The minimal excavation required during installation also helps lessen the environmental impact of the construction process. In challenging ground conditions where traditional retaining wall systems may not be feasible, bored pile walls provide a sustainable solution that balances structural integrity with environmental consciousness.
Construction Process of Bored Pile Walls
To initiate the construction process of bored pile walls, drilling holes into the ground is the first critical step. This process involves specialized equipment and skilled operators to ensure the holes are of the correct diameter and depth.
Once the holes are drilled, the installation techniques for bored pile walls typically include:
- Inserting steel reinforcement cages: Steel cages are carefully placed inside the drilled holes to provide structural strength and stability to the bored pile walls.
- Pouring concrete: High-quality concrete is then poured into the holes, filling them completely and surrounding the steel cages to create a solid foundation.
- Adding anchors or tiebacks: In some cases, additional anchors or tiebacks may be installed to enhance the stability of the bored pile walls, especially in areas with high lateral earth pressures.
Cost analysis for bored pile walls should consider factors such as equipment rental, labor costs, materials, and any additional stabilization measures required for the specific project.
Working Mechanism of Bored Pile Walls
Bored pile retaining walls function by strategically installing closely spaced bored piles to establish a robust structural barrier against soil movement. The design considerations for bored pile walls include factors such as the soil type, groundwater conditions, and the desired wall height.
The soil interaction plays a crucial role in the working mechanism of bored pile walls, as the frictional resistance between the soil and the pile shafts provides the necessary load-bearing capacity. By ensuring proper reinforcement with steel and filling the piles with concrete, these walls gain strength and stability to withstand lateral earth pressures effectively.
The interlocking arrangement of bored piles creates a continuous wall that resists soil movement and retains the surrounding earth. Bored pile walls offer versatility in design, allowing engineers to tailor the wall specifications to accommodate different soil conditions and structural requirements efficiently.
Applications of Bored Pile Retaining Walls
In urban construction projects requiring robust soil retention solutions, bored pile retaining walls serve as vital structural elements. These walls find extensive applications in various urban development projects due to their efficiency and effectiveness.
Here are some key applications of bored pile retaining walls:
- Basement Construction: Bored pile walls are commonly used in urban areas for creating basements in buildings where space is limited, and traditional excavation methods are impractical.
- Slope Stabilization: These walls are effective in stabilizing slopes, preventing landslides, and enhancing the safety of infrastructure in hilly terrains.
- Infrastructure Support: Bored pile retaining walls play a crucial role in supporting embankments for highways, bridges, and railways, providing essential soil retention solutions in congested urban environments.
The versatility and cost-effectiveness of bored pile walls make them a preferred choice for engineers and developers involved in urban development projects requiring robust soil retention solutions.
Factors Influencing Bored Pile Wall Design
Factors influencing the design of bored pile walls include soil conditions, groundwater levels, and adjacent structures, all crucial in determining the structural integrity and stability of the retaining wall system.
The bored pile diameter, spacing, and reinforcement details are vital parameters in wall design, as they directly affect the load-bearing capacity and overall performance.
Additionally, factors such as wall height, excavation depth, and the required load-bearing capacity significantly influence the configuration of bored pile walls. Structural loads, construction sequence, and site constraints also play a pivotal role in determining the design specifics.
It's essential to consider construction methods, material availability, and project timeline during the design phase to ensure the successful implementation of bored pile retaining walls. By carefully evaluating these factors and incorporating them into the design process, engineers can create robust and efficient bored pile wall systems that effectively meet the project requirements.
Comparison With Other Retaining Wall Types
When comparing bored pile retaining walls to other types, it becomes evident that each has distinct advantages and limitations in specific soil conditions and project requirements.
Bored pile walls offer greater depth capabilities compared to sheet piled walls, making them suitable for projects requiring deeper excavation support.
Secant walls and piles excel in water resistance, providing a more watertight solution compared to contiguous walls and piles, which is crucial in environments with high water levels. However, in cohesive soils, contiguous walls and piles are more cost-efficient than secant walls, offering a more economical option for certain projects.
King post walls stand out for their flexibility in shape and installation around obstructions, providing adaptability in challenging site conditions.
Bored pile walls, on the other hand, shine in their adaptability to different wall layouts and thicknesses, offering versatility in design configurations for various project needs.
Maintenance and Longevity of Bored Pile Walls
To ensure the optimal performance and longevity of bored pile walls, regular inspection and proactive maintenance practices are essential components of a comprehensive asset management strategy. Preventive measures play a crucial role in identifying early signs of distress or potential issues, allowing for timely intervention.
Implementing proper maintenance, such as repairing concrete cracks and addressing drainage problems, can significantly extend the lifespan of bored pile walls. Additionally, the utilization of cathodic protection systems helps prevent corrosion of reinforcement bars, enhancing the overall durability of the structure.
A robust maintenance plan should include periodic cleaning, vegetation control, and structural assessments to ensure the long-term performance of bored pile walls. Addressing water infiltration and drainage issues promptly is vital to prevent water-related damage and maintain the stability and effectiveness of bored pile retaining walls over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is the Purpose of Bored Piling?
When you think about bored piling, remember it's all about stabilizing soil and designing solid foundations. It's about enhancing load-bearing capacity for deep excavations. Bored piling ensures your structure stands strong on stable ground.
What Are the Problems With Bored Pile Construction?
When dealing with bored pile construction, you may encounter challenges like soil stability issues affecting deep excavations. These problems can lead to cost overruns and construction delays, impacting the overall project timeline and budget.
How Are Bored Piles Installed?
When installing bored piles, you use specialized equipment to drill into the ground, displacing soil. This process involves precise drilling techniques to ensure proper pile installation. The equipment plays a crucial role in achieving the required depth for the piles.
When Should Bored Piles Be Used?
When should you use bored piles? Utilize them for soil stability during construction. Ensure foundation stability with bored pile retaining walls. Opt for this technique in challenging ground conditions where traditional methods may not suffice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, bored pile retaining walls are an efficient and versatile solution for stabilizing excavations in urban areas with limited space. By transferring lateral soil pressures to the piles, these walls prevent collapse and maintain the stability of the surrounding soil.
With their effective construction process and wide range of applications, bored pile walls are a reliable choice for retaining structures in various ground conditions. Proper maintenance and attention to design factors ensure the longevity and effectiveness of these structures.
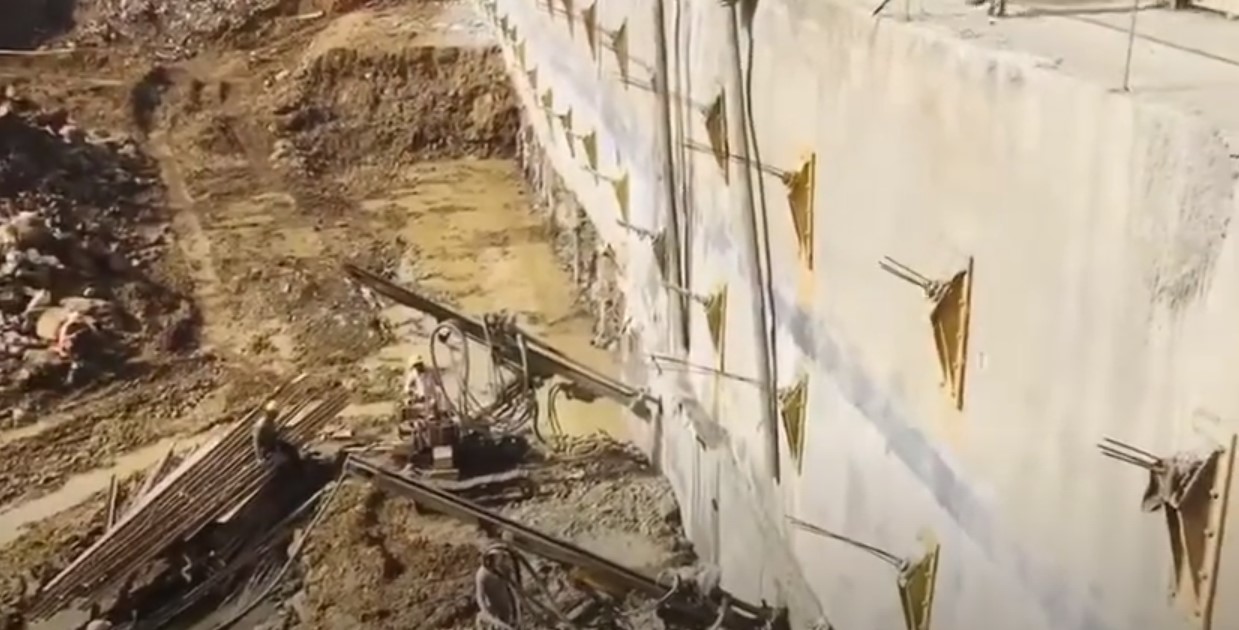
Diaphragm walls are a type of retaining wall used to provide support for excavations and structures. They consist of reinforced concrete panels constructed in situ, by excavating a narrow trench that is continuously filled with a bentonite slurry to provide support. Reinforcement cages are lowered into the slurry-filled trench, and concrete is tremied into the trench through the slurry.
The result is a continuous underground reinforced concrete wall that can resist significant earth pressures and water pressures. Diaphragm walls provide support and groundwater cutoff for the retained soil, allowing the construction of foundations and basements in difficult soil conditions.
Diaphragm walls are ideal for applications like underground parking garages, structural foundations in soft soils, and excavation support for tunnels and shafts. Their ability to be constructed in dense urban environments with minimal vibration makes them well-suited for cities.
Key Takeaways
- Exceptional lateral support crucial for deep excavation integrity
- Versatile in various soils, ideal for urban areas
- Efficient space utilization in congested settings
- High resistance to lateral pressure ensures excavation safety

Strength and Stability of Diaphragm Walls

When considering the strength and stability of diaphragm walls in deep excavations, their exceptional lateral support capabilities play a crucial role in ensuring structural integrity against soil pressures at significant depths.
Construction techniques and material selection are vital aspects in enhancing the strength of diaphragm walls. The construction process involves excavating a trench, installing reinforcement, and pouring concrete into the trench to form the wall. Proper material selection, such as high-strength concrete and quality reinforcement, is essential to withstand the immense pressures exerted on the walls in deep excavations.
Monitoring systems and safety measures are integral components to guarantee the stability of diaphragm walls throughout the excavation process. Advanced monitoring systems, including inclinometers and extensometers, help track wall movements and detect any potential issues promptly. Implementing stringent safety measures, such as regular inspections and adherence to industry regulations, ensures a secure working environment and minimizes risks associated with deep excavation projects.
Versatility in Deep Excavation Projects

In deep excavation projects, the versatility of diaphragm walls becomes evident through their adaptability to various soil types and rocks, offering a reliable solution for complex underground construction challenges. Diaphragm walls provide cost-effective solutions and environmental benefits, making them an ideal choice for deep excavation projects. Here are three key points highlighting the versatility of diaphragm walls:
- Adaptability to Various Soil Types: Diaphragm walls can be constructed in a wide range of soil conditions, including soft soils, hard rocks, and mixed face conditions, ensuring stability and strength in diverse environments.
- Suitability for Urban Areas: Their quiet construction process and minimal vibration make diaphragm walls ideal for urban areas where noise and disturbance need to be minimized, showcasing their versatility in sensitive environments.
- Foundation and Retaining Wall in One: Diaphragm walls serve a dual purpose by acting as both the foundation for superstructures and the external walls for basements, optimizing space and providing a structurally sound solution.
Efficient Space Utilization With Diaphragm Walls
The compact design of diaphragm walls facilitates efficient space utilization, making them a top choice for deep excavation projects in urban environments with limited construction areas. Diaphragm walls require minimal space compared to traditional excavation methods, allowing for deep excavations in congested city settings without disrupting nearby structures.
By employing vertical construction techniques, diaphragm walls enable the optimization of space, particularly in tight urban locations. Their small footprint permits the construction of deep foundations close to existing buildings, maximizing land use efficiency in densely populated areas where space is at a premium.
This efficient use of space not only ensures the completion of deep excavation projects but also integrates well with the urban environment, showcasing the adaptability of diaphragm walls in maximizing efficiency and urban integration. For projects requiring deep excavations in constrained spaces, diaphragm walls offer a practical solution that harmonizes with the surrounding urban landscape.
High Resistance to Lateral Pressure
With their reinforced concrete structure, diaphragm walls exhibit exceptional resistance to high lateral pressures, making them a reliable choice for deep excavation projects. When it comes to soil retention and excavation safety, diaphragm walls excel in providing the necessary support and stability.
Here are three key reasons why diaphragm walls are highly resistant to lateral pressure:
- Reinforced Concrete Structure: The robust construction of diaphragm walls with reinforced concrete ensures they can withstand substantial earth pressures, maintaining the integrity of the excavation site.
- Deep Excavation Compatibility: Diaphragm walls are designed to endure significant lateral forces at deep excavation depths, making them ideal for projects where soil movement must be prevented.
- Stability and Strength: The depth and thickness of diaphragm walls play a crucial role in their ability to resist lateral pressure effectively, enhancing excavation safety and overall project stability.
Ideal for Urban Areas and Limited Spaces
Enhancing urban construction efficiency, diaphragm walls prove indispensable in confined spaces due to their exceptional adaptability and structural integrity. In urban areas with limited space, these walls offer a cost-effective solution by maximizing land use efficiency.
Their ability to be constructed at great depths without the need for extensive dewatering makes them ideal for densely-populated areas where access to drainage systems is restricted. Diaphragm walls minimize disturbance during construction, reducing vibration and noise levels that could disrupt urban activities.
The water-tight construction of these walls eliminates the need for dewatering, a significant advantage in urban settings. Serving as both external walls for basements and foundations for superstructures, diaphragm walls provide stability and support in confined spaces where lateral loads are high.
Their design ensures they can withstand the pressures associated with deep excavations, making them a reliable choice for urban projects requiring structural integrity and minimal disturbance.
Deep Construction Depth Capabilities
Unveiling the unparalleled depths achievable by diaphragm walls, their construction capabilities extend to an impressive 100 meters, solidifying their status as the go-to solution for deep excavation projects. When considering deep construction depth capabilities, diaphragm walls stand out due to their exceptional features:
- Structural Support: Diaphragm walls offer the capability to construct walls at depths exceeding 80 meters, providing reliable structural support even in challenging conditions.
- Lateral Earth Support: Ideal for deep excavations, these walls can be designed with integral waler beams and anchor block outs, addressing construction challenges related to lateral earth support.
- Cost-Effective Solution: Diaphragm walls are known for their ability to support very high lateral loads, making them a cost-effective choice for deep excavation projects where stability and strength are crucial.
With widths ranging between 450mm and 1500mm, these walls ensure flexibility in design and application, making them a versatile and efficient option for deep excavations.
Suitability for Various Project Types
Transitioning from their deep construction depth capabilities, diaphragm walls demonstrate remarkable versatility by being suitable for a wide array of project types, owing to their ability to support high lateral loads and provide reliable structural support.
These walls prove cost-efficient as they serve as permanent retaining structures, eliminating the need for additional support systems in projects like basement walls, parking garages, and tunnel access shafts. The low permeability of diaphragm walls not only aids in seepage control but also enhances environmental benefits by preventing groundwater contamination.
Their adaptability for top-down construction methods further enhances cost efficiency by reducing construction time and complexity. Additionally, the ability to install diaphragm walls close to existing structures with limited headroom showcases their flexibility across various project types, ensuring efficient space utilization while maintaining structural integrity.
Incorporating integral waler beams and anchor block outs in the design further underlines the high-quality support these walls provide, making them a reliable choice for a wide range of construction projects.
Enhanced Support for Underground Structures
For underground structures requiring enhanced support, diaphragm walls offer superior lateral stability and vertical load-bearing capabilities. When it comes to ensuring the safety and stability of underground constructions, diaphragm walls stand out as cost-effective solutions that provide unmatched support. Here's why they excel in supporting underground structures:
- Improved Safety: Diaphragm walls are known for their exceptional lateral support, reducing the risk of structural failures and ensuring a safe environment for underground operations.
- Cost-Effective Solutions: By offering both lateral stability and vertical load-bearing capabilities, diaphragm walls provide a comprehensive support system that minimizes the need for additional reinforcement measures, saving costs in the long run.
- Enhanced Load-Bearing Capacity: The reinforced concrete panels used in diaphragm walls are designed to withstand high vertical loads, making them ideal for supporting heavy superstructures with confidence and reliability.
Why Choose Us for Diaphragm Wall Construction in New Zealand
When it comes to constructing robust diaphragm walls in New Zealand, our expertise stands unparalleled. We specialize in delivering high-strength, versatile diaphragm wall solutions tailored for both urban environments and challenging soil conditions. Our approach combines state-of-the-art construction techniques with meticulous planning and quality materials, ensuring each project benefits from exceptional lateral support and stability.
Our diaphragm walls are designed to withstand significant earth and water pressures, making them ideal for a wide range of applications including underground parking, foundations in soft soils, and excavation support for tunnels. In dense urban settings, our techniques offer the dual benefits of minimal vibration and efficient space utilization, preserving the urban landscape while optimizing construction areas.
As a team of skilled professionals, we pride ourselves on our ability to navigate New Zealand's unique geological challenges, delivering environmentally sensitive and cost-effective solutions. Choose us to ensure your deep excavation projects are built on a foundation of reliability and excellence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are the Advantages of Diaphragm Wall?
Diaphragm walls offer cost efficiency and construction speed, minimizing environmental impact. Their sleek design enhances aesthetic appeal. You benefit from their versatility in deep excavation projects, supporting high lateral loads and water-tight structures without dewatering.
What Are Diaphragm Walls and Why Is It Important in the Excavation Process?
Diaphragm walls, constructed using hydraulic grabs and bentonite slurry, provide stability for deep excavations. They save costs by eliminating dewatering needs and offer environmental benefits. Stability analysis ensures their effectiveness in supporting structures and preventing soil movement.
How Deep Can Diaphragm Walls Go?
Exploration depth of diaphragm walls can exceed 100 meters, utilizing advanced construction techniques. Panels, ranging from 450mm to 1500mm, provide solid structural support. Tight joint tolerances ensure secure connections for deep excavation projects, handling high lateral loads effectively.
What Are the Characteristics of a Diaphragm Wall?
When considering the characteristics of a diaphragm wall, focus on its construction techniques like panel excavation with hydraulic grabs and concrete pouring via tremie pipes. Its structural integrity and waterproofing properties are key for soil retention.
Conclusion
Diaphragm walls stand out as the optimal choice for deep excavations due to their unmatched strength, stability, and versatility.
With high resistance to lateral pressure, deep construction depth capabilities, and efficient space utilization, these walls prove essential in urban areas and limited spaces.
Their ability to support underground structures effectively makes them a reliable solution for various project types.
Overall, diaphragm walls offer a comprehensive and efficient solution for deep excavation projects.